Korean ginseng boasts a rich history dating back to the Three Kingdoms period in Korea. During that era, Koreans traditionally consumed raw sun-dried ginseng, despite its relatively short shelf life. It was under the reign of King Munjong of the Goryeo dynasty that a pivotal processing technique was devised, involving the steaming and subsequent drying of ginseng. This innovation significantly extended the herb's shelf life and amplified its medicinal properties. Due to the historical nomenclature of the Korean peninsula as Goryeo during that period, the ginseng cultivated in Korea earned the monikers "Goryeo Red Ginseng" or "Korean Red Ginseng."
Warm

Heart

Spleen
Lungs
Kidney

Sweet

Bitter
Promote blood circulation, anti-fatigue and anti-stress, boost immunity, regulate blood pressure
| . | Improve Platelet Aggregation Research indicates that blood clot formation is influenced by the level of platelet aggregation triggered by thrombin. Red ginseng's aqueous extract has demonstrated the ability to prevent thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, thereby exhibiting anti-thrombotic properties. Korean Red Ginseng is particularly noteworthy for its enhanced effectiveness in comparison to red ginseng extracts derived from China and Japan.
|
| . | Promotes Blood Circulation to Skin The extract of Korean Red Ginseng is known for its capacity to be gradually absorbed by the skin and its capability to widen capillaries, facilitating improved blood circulation in the skin. This heightened blood flow can boost the transport of nutrients to the skin, maintain the skin's moisture and oil equilibrium, ward off dehydration, roughness, and wrinkles while enhancing skin elasticity. Furthermore, the active constituents present in red ginseng possess the ability to hinder melanin production, leading to a more radiant and smoother complexion.
|
| . | Anti-fatigue and anti-stress Korean Red Ginseng is rich in 38 varied ginsenosides, particularly those from the Panaxadiol family. These ginsenosides are renowned for their anti-fatigue and anti-stress attributes. They are thought to aid in enhancing memory and learning capabilities, boosting physical endurance, and providing protection against radiation, all of which are beneficial effects.
|
| . | Enhance Immune Function During the mid-1980s, researchers isolated an acidic polysaccharide known as RGAP (Red Ginseng Acidic Polysaccharide) from Korean Red Ginseng, exhibiting notable immunomodulatory properties. RGAP is recognized for its significant role in boosting immune function, thereby enhancing the body's immune response.
|
| . | Controlling Diabetes Substances found in Korean red ginseng have been identified to stimulate insulin secretion and exhibit insulin-like effects. Among these substances, ginsenosides have shown promise in enhancing high blood sugar levels and effectively managing the onset of diabetes.
|
| . | Regulates Blood Pressure Korean Red Ginseng possesses vasodilatory properties, aiding in the dilation of blood vessels and enhancing blood circulation. The ginsenoside components present in Korean Red Ginseng are thought to stimulate the release of nitric oxide from endothelial cells, potentially leading to a reduction in blood pressure.
|
| . | Strengthen and Protect the Liver Components found in Korean Red Ginseng exhibit anti-hepatitis activity, detoxification properties, and the ability to protect and stimulate liver regeneration and recovery, which collectively support liver health. Moreover, Korean Red Ginseng has a traditional application for alleviating hangover symptoms and aiding in alcohol detoxification.
|
| . | Antioxidant Korean Red Ginseng contains the active antioxidant compound known as 2-methyl-3-hydroxy-4H-pyran-4-one, or maltol. Maltol is recognized for its potent antioxidant properties, offering protection against oxidative damage in various body tissues. Specifically, in cardiac cells, maltol can safeguard the cell membrane from adriamycin-induced damage. In hepatocytes, it exhibits a protective effect against toxicity induced by paraquat. Furthermore, maltol has been shown to protect against reperfusion injury in the heart by reducing oxidative damage, a process that occurs when blood flow is reinstated following a period of ischemia.
|
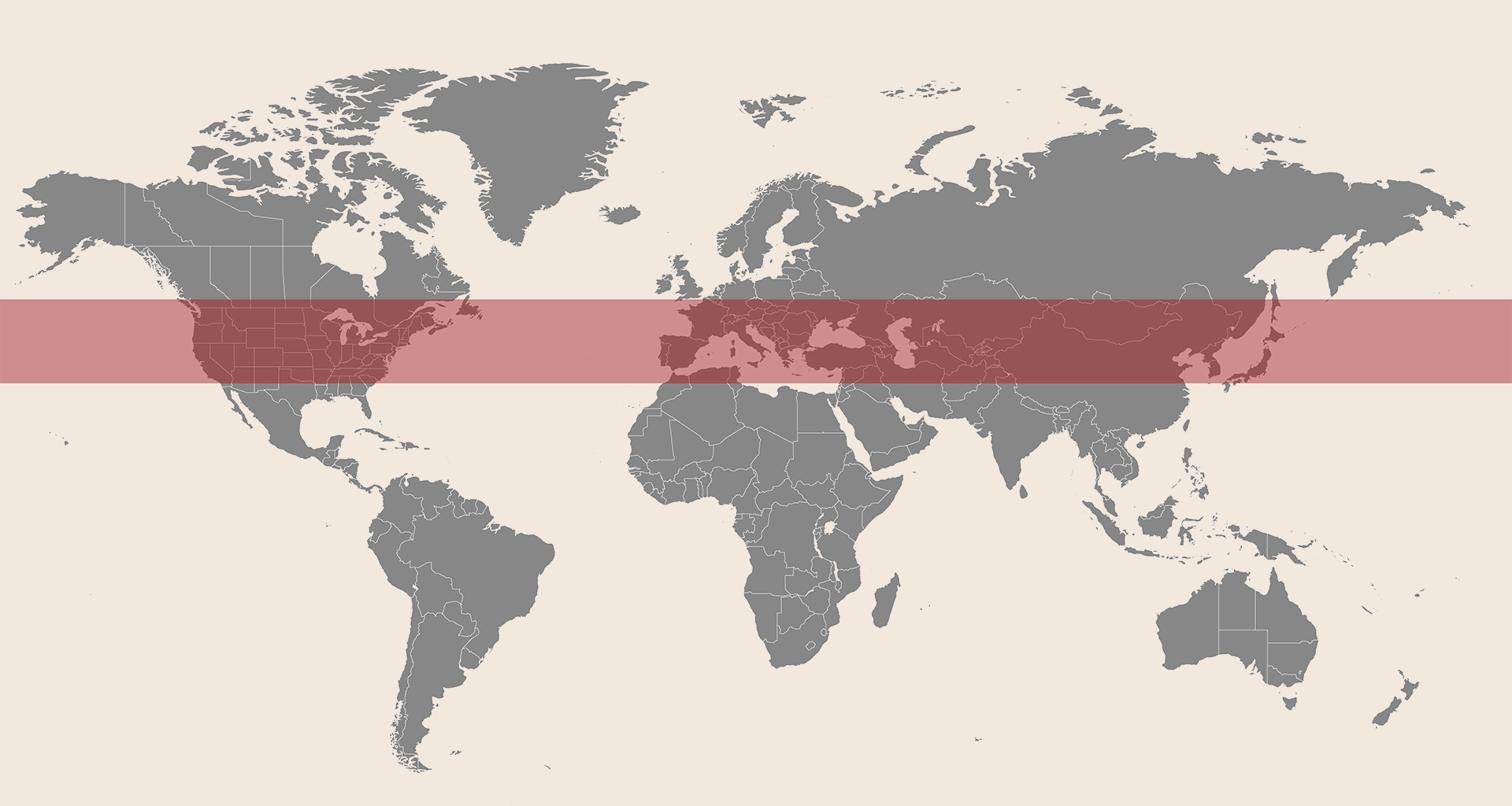
Korean Red Ginseng is crafted using raw ginseng as its primary ingredient, sourced from cultivation in the northeastern areas of China, Japan, and Korea. Disparities in the steaming techniques employed can lead to variations in the quality of red ginseng products. Given Korea's recognized leadership in the processing methodologies of red ginseng, Korean Red Ginseng tends to exhibit a comparatively elevated quality level.
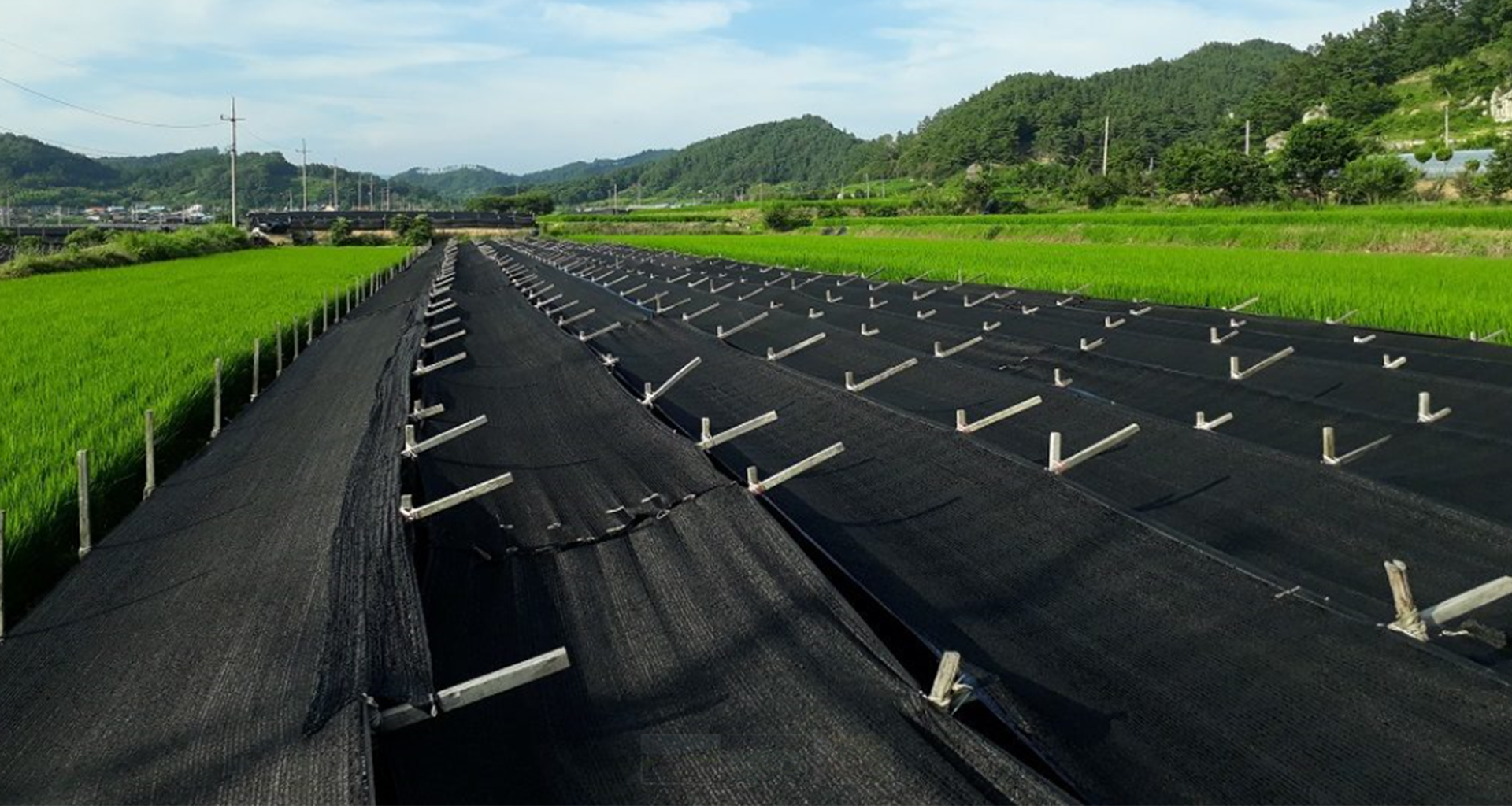

01 The cultivation of Korean Red Ginseng is a lengthy process. The ideal soil moisture content for the growth of red ginseng is around 60% of the soil's water-holding capacity.
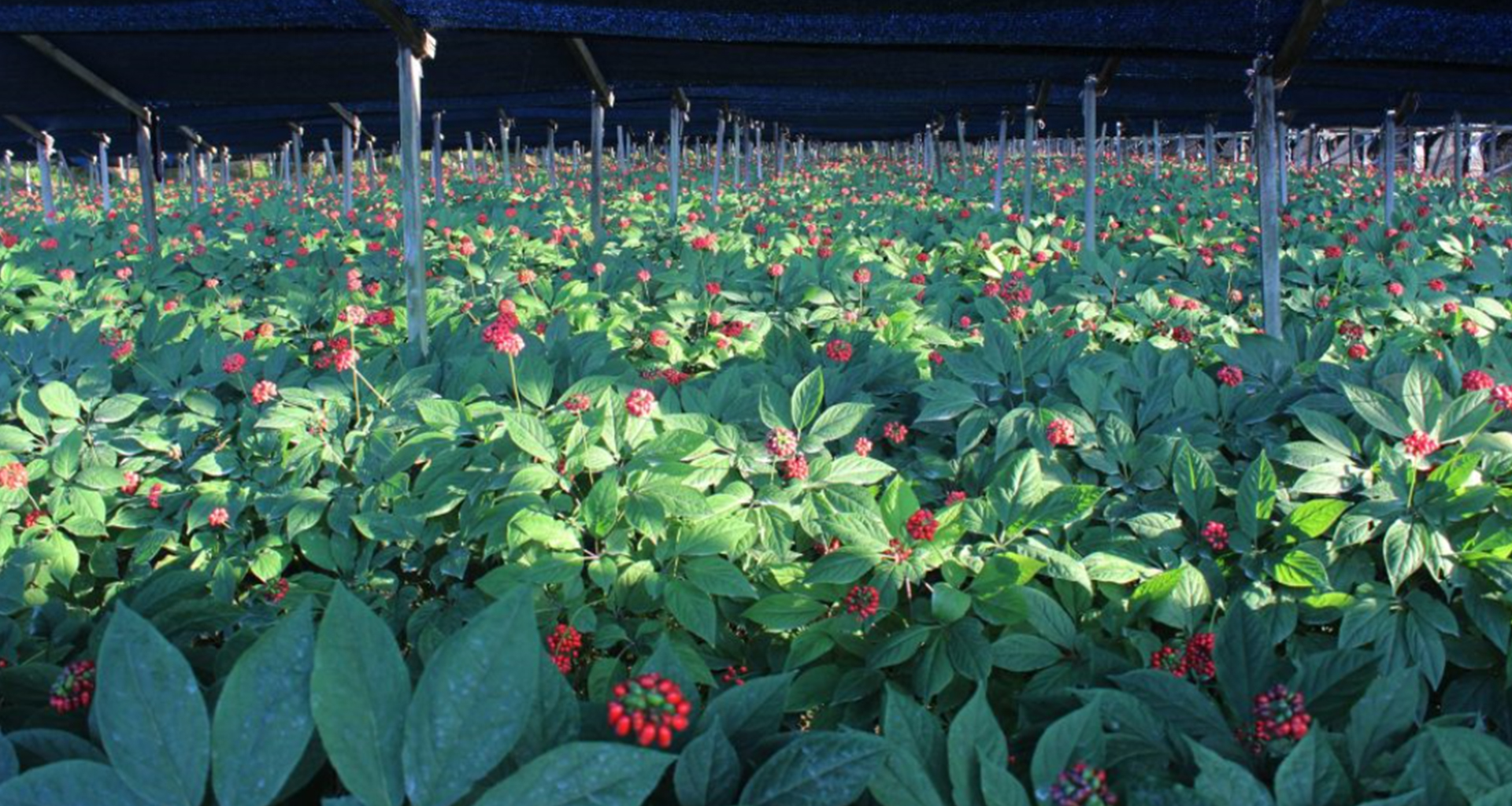

02 When transplanting red ginseng seedlings into the soil, it is recommended to select high-quality seedlings and plant them at a 45-degree angle. This planting method encourages the development of a robust taproot and two lateral roots, resulting in a human-shaped ginseng root with thick main roots.
_1.jpg)
03 The number of palmate compound leaves of red ginseng varies depending on its growth age. Generally, a 1-year-old red ginseng plant has one leaf, a 2-year-old plant has two leaves, a 3-year-old plant has three leaves, a 4-year-old plant has four leaves, a 5-year-old plant has five leaves, and a 6-year-old plant has six leaves.
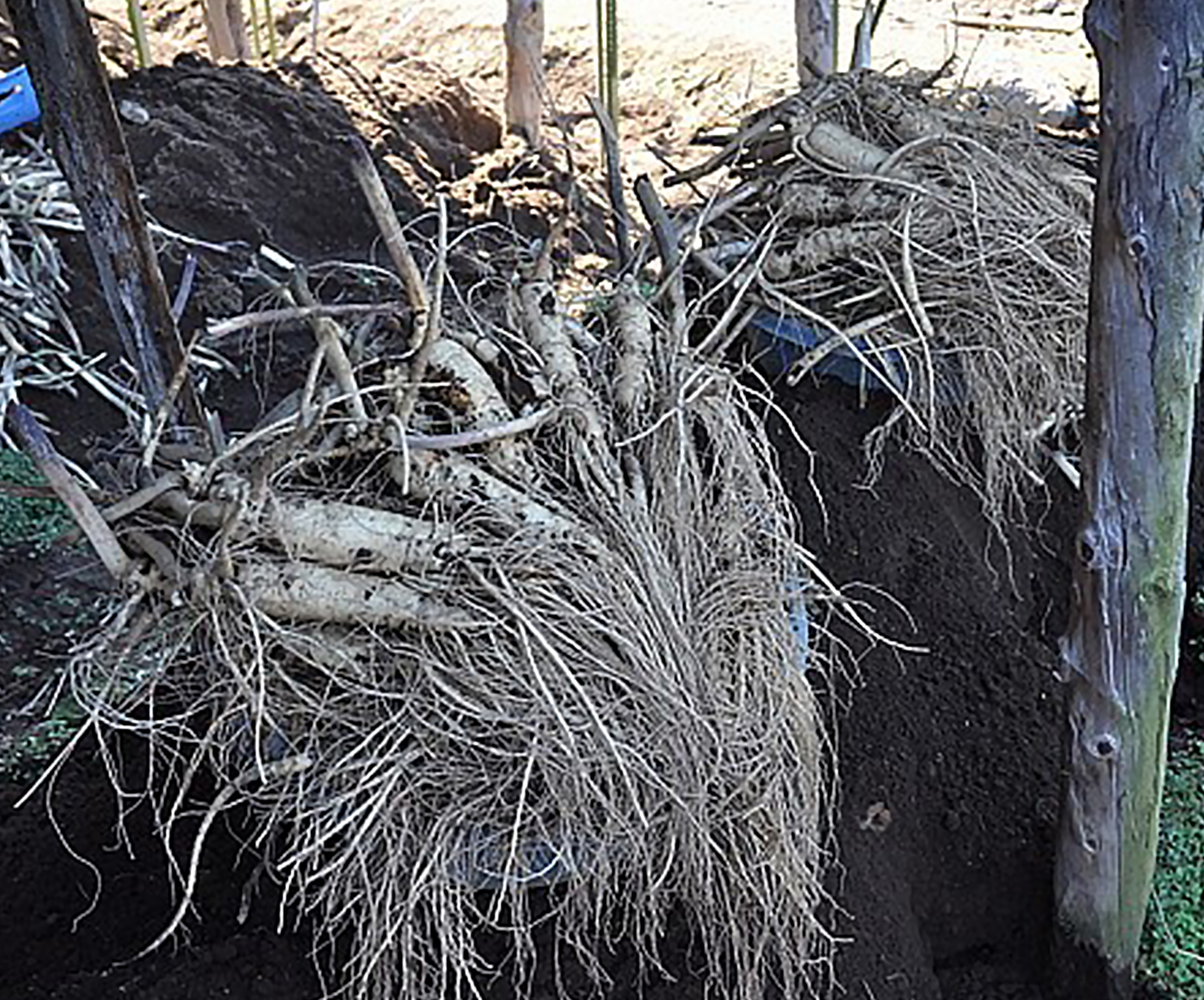

04 The period between September and November, after six years of growth, is considered the optimal harvesting time for Korean Red Ginseng. During this time, the various components and active compounds of red ginseng reach their highest levels, making it an ideal time for harvest.
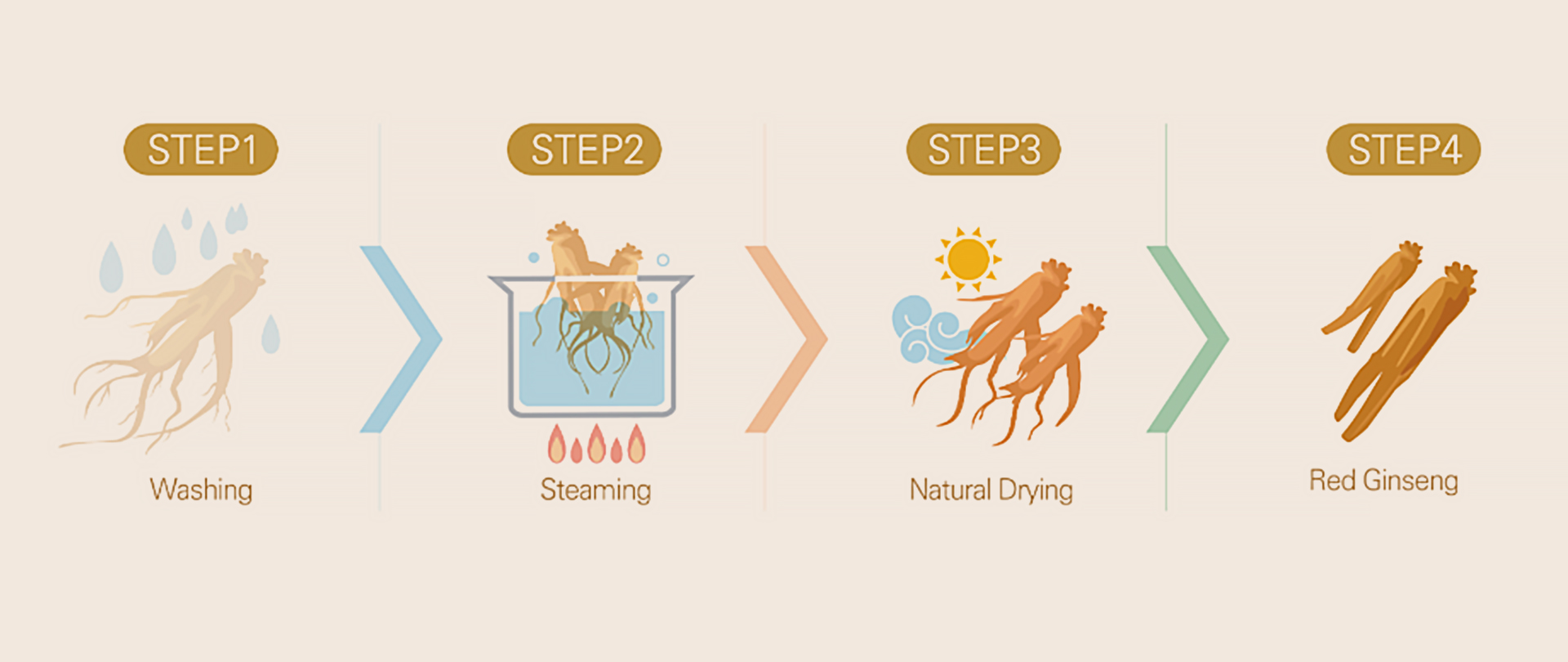
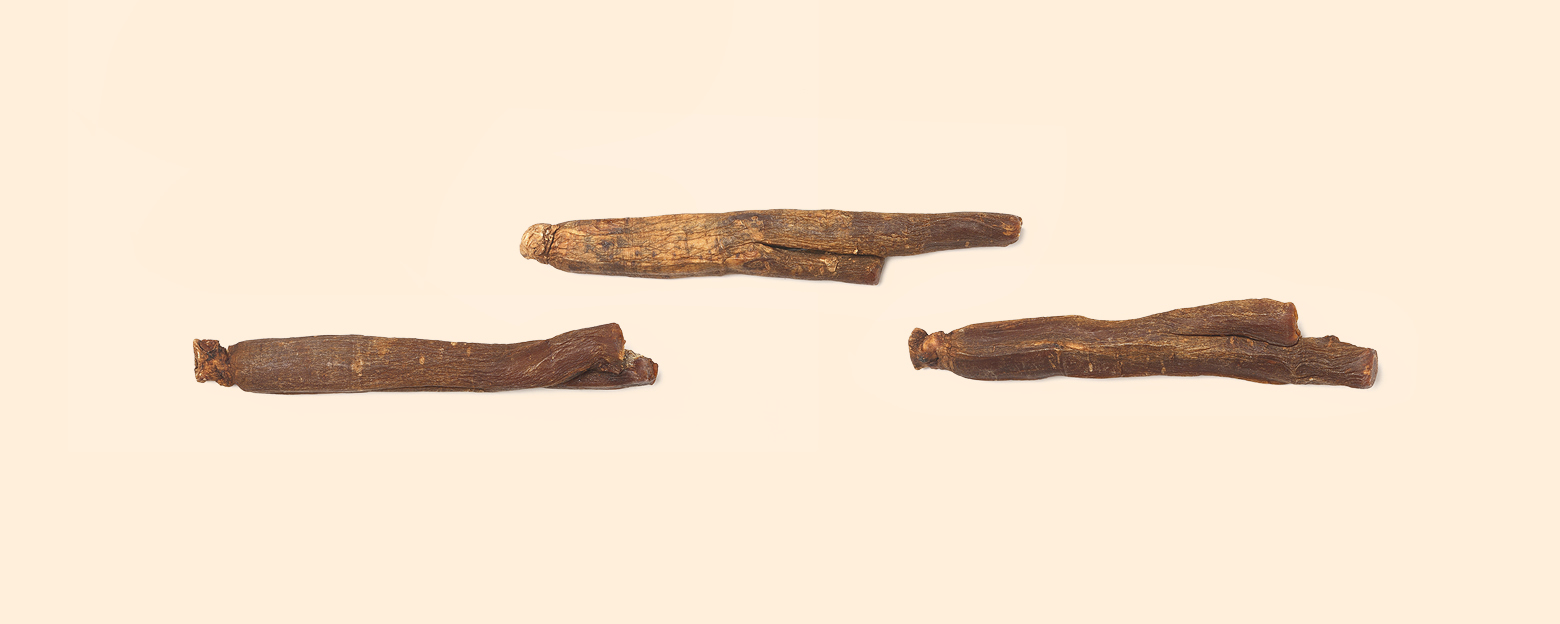
When fresh 6-year-old ginseng is steamed and subsequently dried to reduce its moisture content to below 15%, it undergoes a transformation to a deep brown color. This process effectively eliminates any risk of decay. Not only does this method prolong the storage life of ginseng, but it also greatly intensifies its aroma and boosts the levels of antioxidant compounds present in the ginseng.















