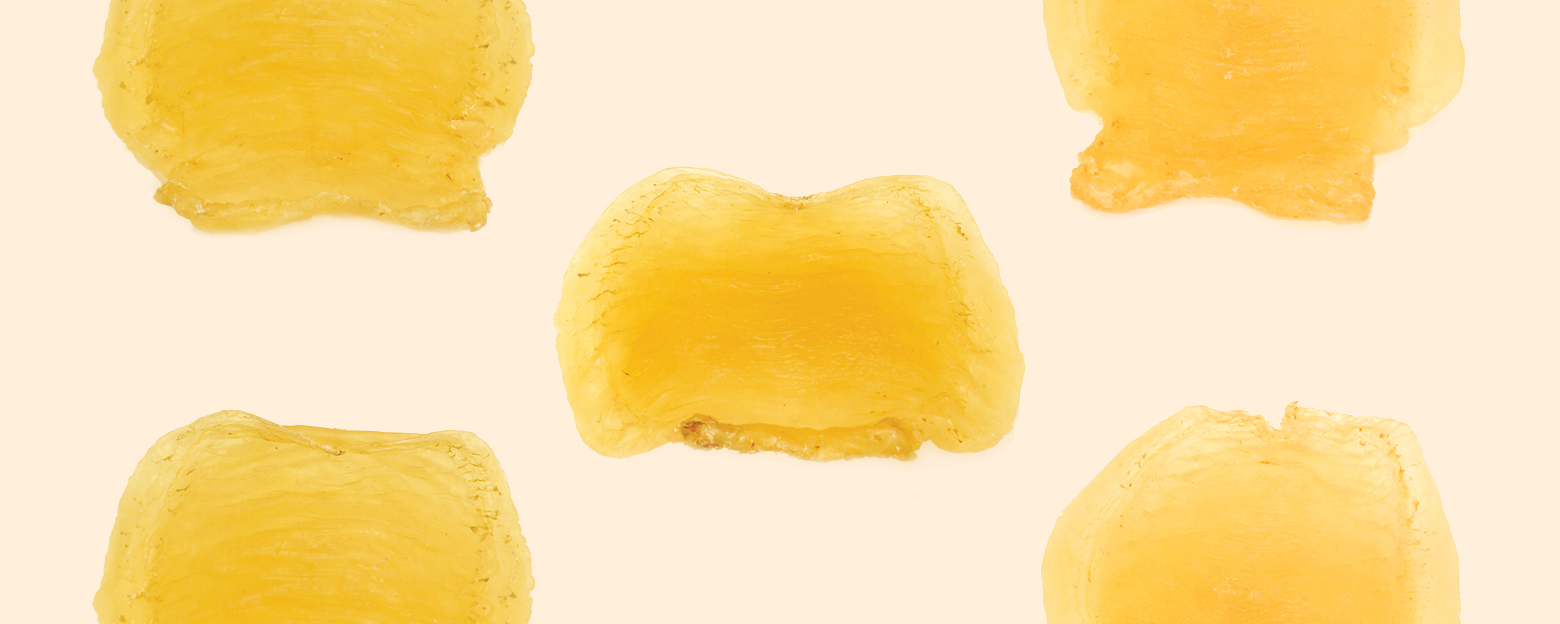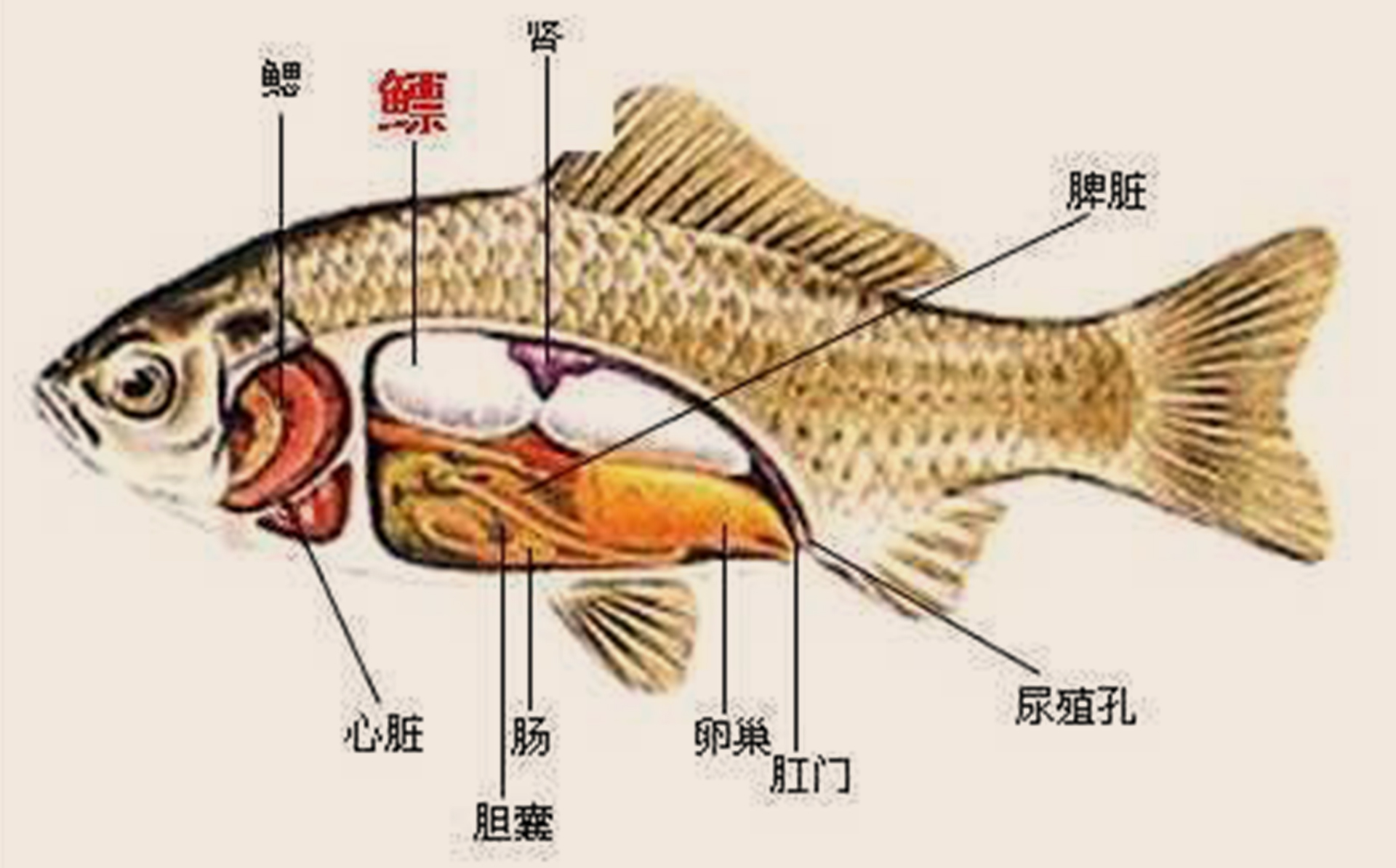
Fish maw is an organ found in fish that helps control their buoyancy. It is rich in collagen and gelatinous substances, which gives it a gelatin-like texture and consistency. Due to its unique properties and culinary uses, it is a popular ingredient in Chinese cuisine and is often used in soups, stews, and braised dishes for its texture and nutritional benefits.
The consumption of fish maw by Chinese people can be traced back to before the Han Dynasty. The ancient book "Qimin Yaoshu" contains records of fish maw. Fish maw has always been considered a precious traditional Chinese delicacy and is classified as one of the "Eight Treasures of the Sea," which includes abalone, sea cucumber, shark's fin, and fish maw.

Plain

Liver
Kidney

Sweet
Fish maw is believed to have several health benefits, including: promoting wound healing, supporting a favorable environment for egg implantation, enhancing gastrointestinal digestion and absorption, nourishing Yin and promoting beauty and brain function.
| . | Promotes wound healing Some studies have shown that fish maw contains glycosaminoglycans, including chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate. Chondroitin sulfate is believed to contribute to the repair, regeneration, and healing of skin tissue. When combined with its interaction with "high-quality proteins" in fish maw, it may enhance the ability to transport nutrients in the blood and promote blood clotting. Consuming fish maw 15-20 days after surgery has been suggested to promote wound healing and provide nourishment and anti-aging benefits to the body, potentially contributing to longevity.
|
| . | Helps provide a good environment for egg implantation Fish maw contains arginine, which can help relax smooth muscle cells in blood vessels, leading to vasodilation and potentially lowering blood pressure. In terms of fertility, arginine is believed to improve blood circulation to the uterus and ovaries. This can potentially enhance the production of higher quality eggs and provide a more favorable environment for the implantation of fertilized eggs.
|
| . | Enhance gastrointestinal digestion and absorption Fish maw is rich in high-quality collagen protein, which is easily absorbed by the human body and can also help protect the gastrointestinal mucosa. It can promote intestinal peristalsis, enhance the digestive and absorptive functions of the gastrointestinal tract, and alleviate digestive disorders and loss of appetite caused by modern work stress and irregular eating habits.
|
| . | Nourish yin and skin As we age and due to environmental changes, the collagen protein in the deeper layers of the skin gradually depletes. The high-quality collagen protein found in fish maw can effectively replenish the lost collagen in the body, helping to maintain smooth and elastic skin.
|
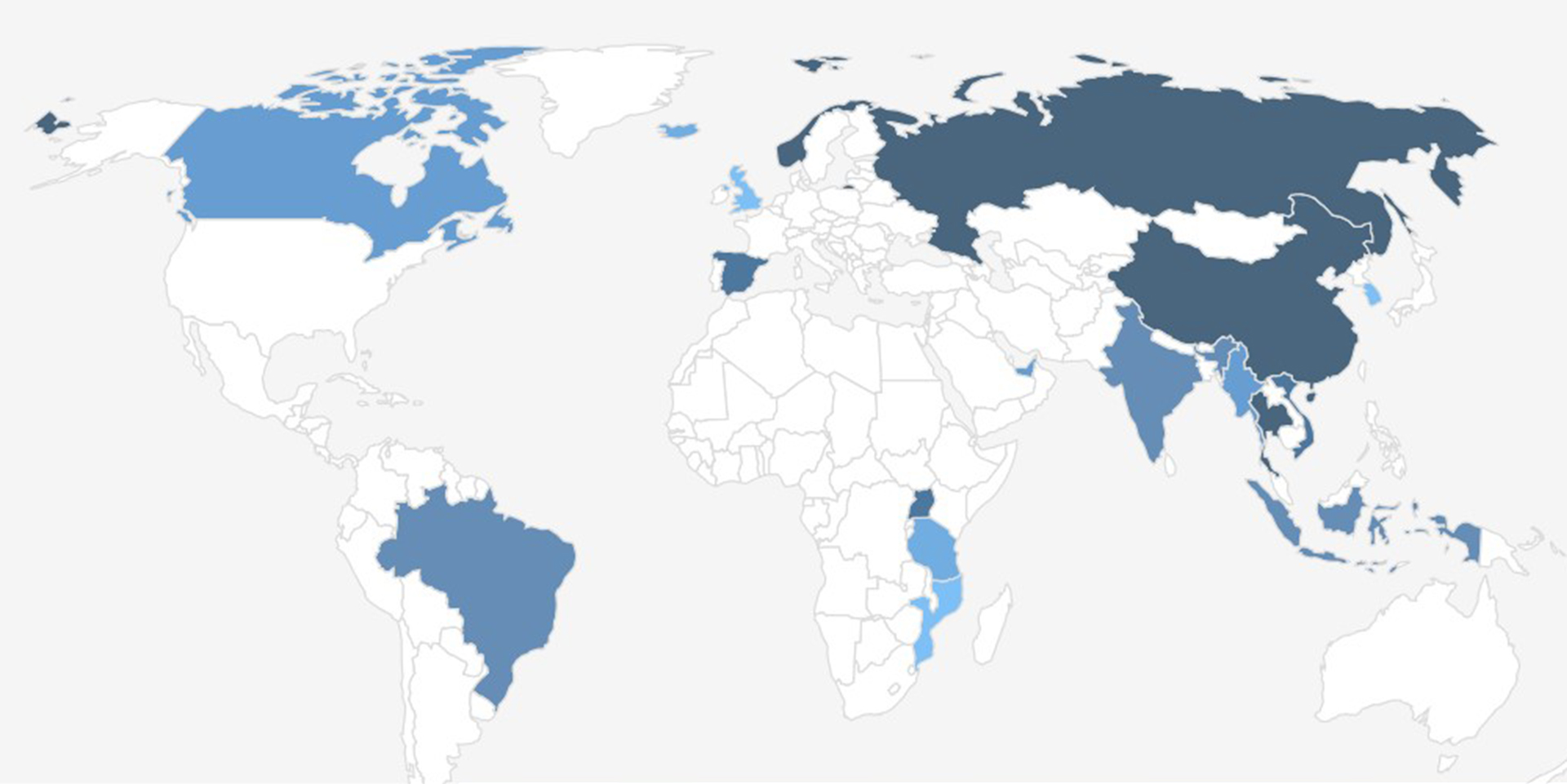
There is a wide variety of fish maw, which can differ based on their origin and the species of fish they come from. The main production areas include Africa, Pakistan, India, and other regions. In particular, the waters off the coast of Guangdong in China are known for producing high-quality fish maw. The marine environment in this area is a mix of saltwater and freshwater, resulting in a higher natural mineral content compared to fully saline waters. Among the varieties, the "Jinqian Du" (literally "money bladder"), which is found in the Humen Sea area, is particularly prized and commands a high price due to its excellent quality.

01 After the fishing boat returns to shore, the fish catch is immediately processed; otherwise, the fish maw will develop a strong fishy odor and affect the texture of the fish maw.

02 When the fish catch is brought onboard the fishing vessel, it is often poured into a machine for cleaning.
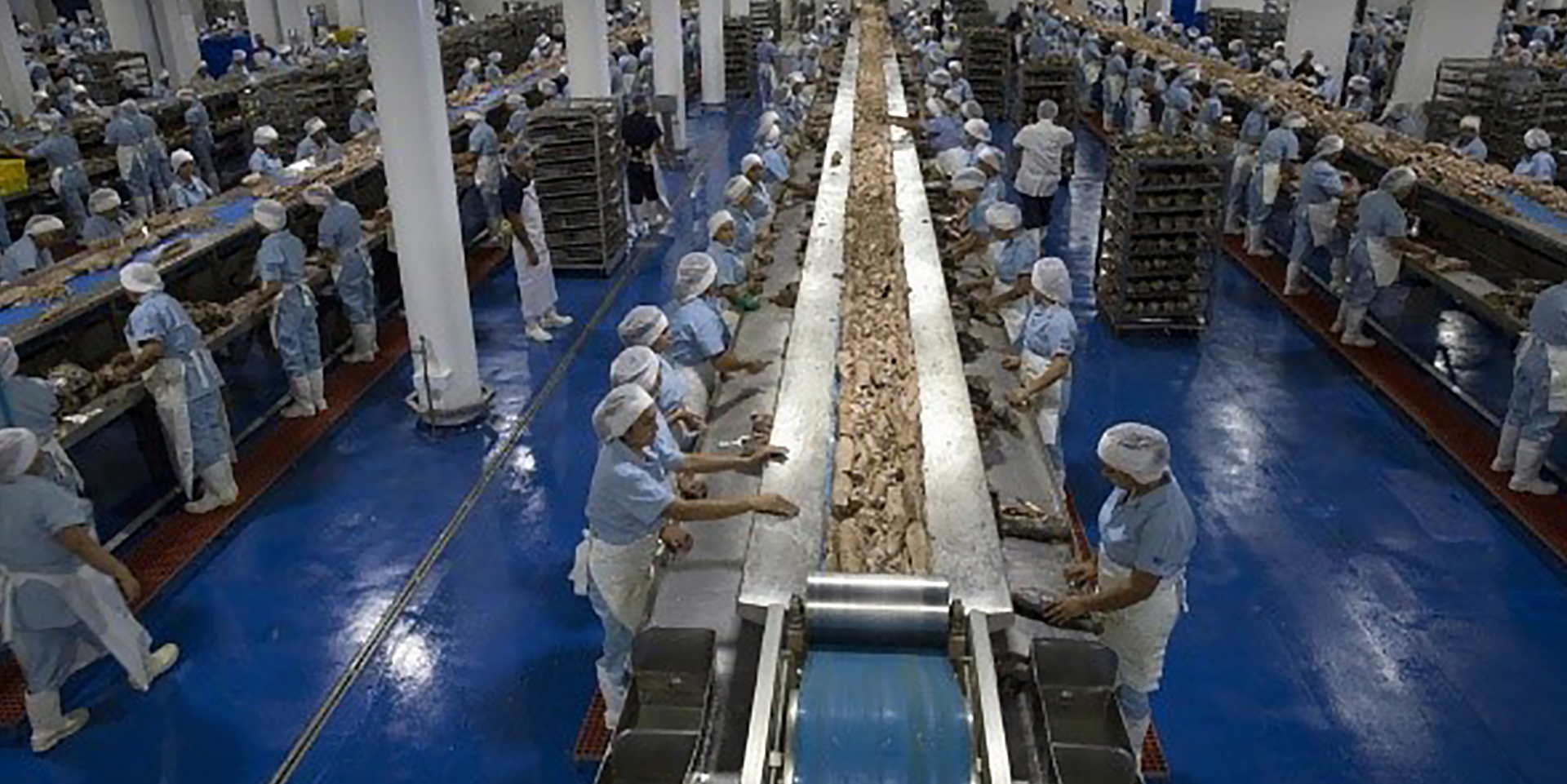

03 The catch is transported to factory for further processing.
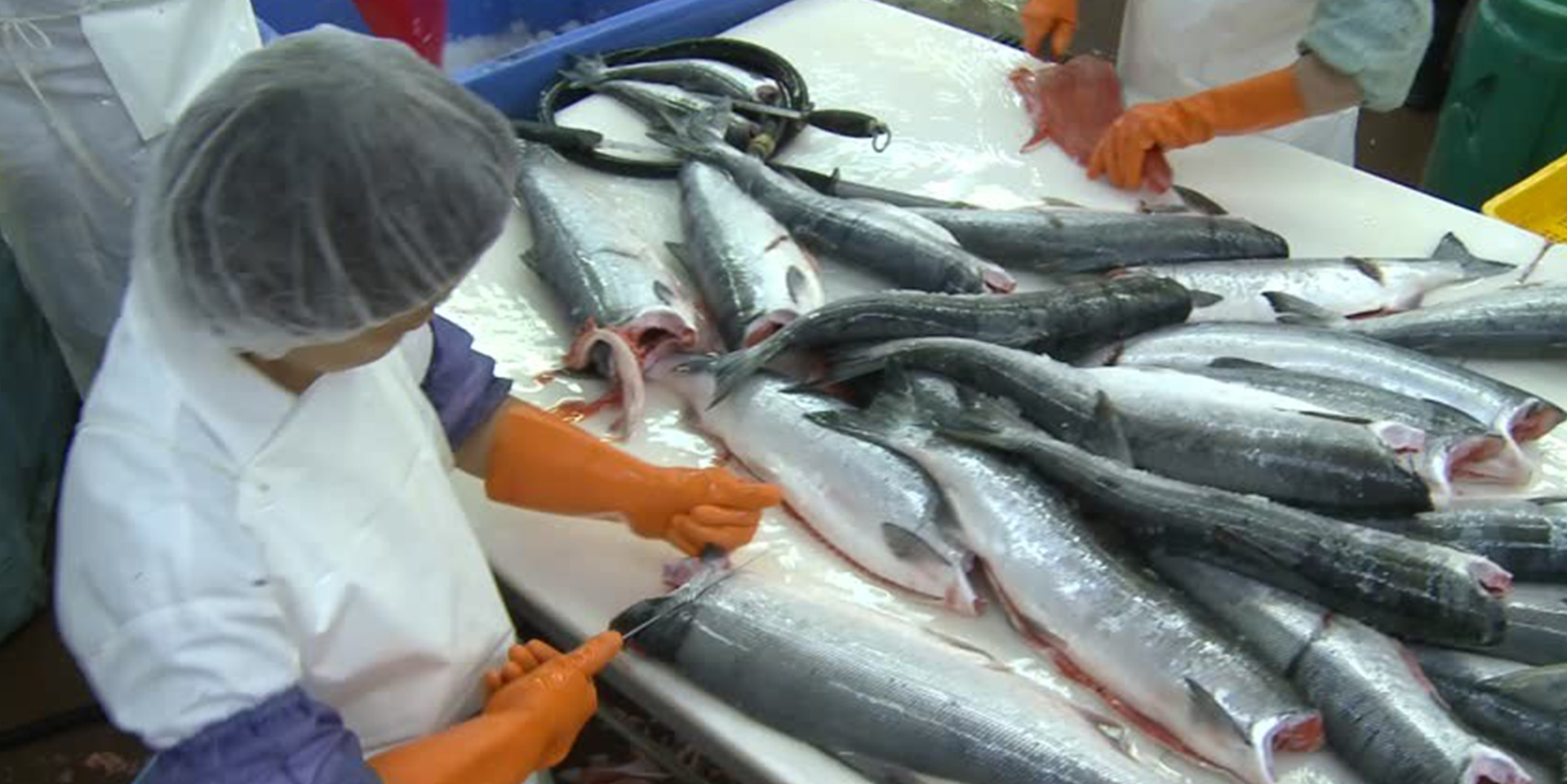

04 Fillet the fish, clean and pack for sale in different markets.
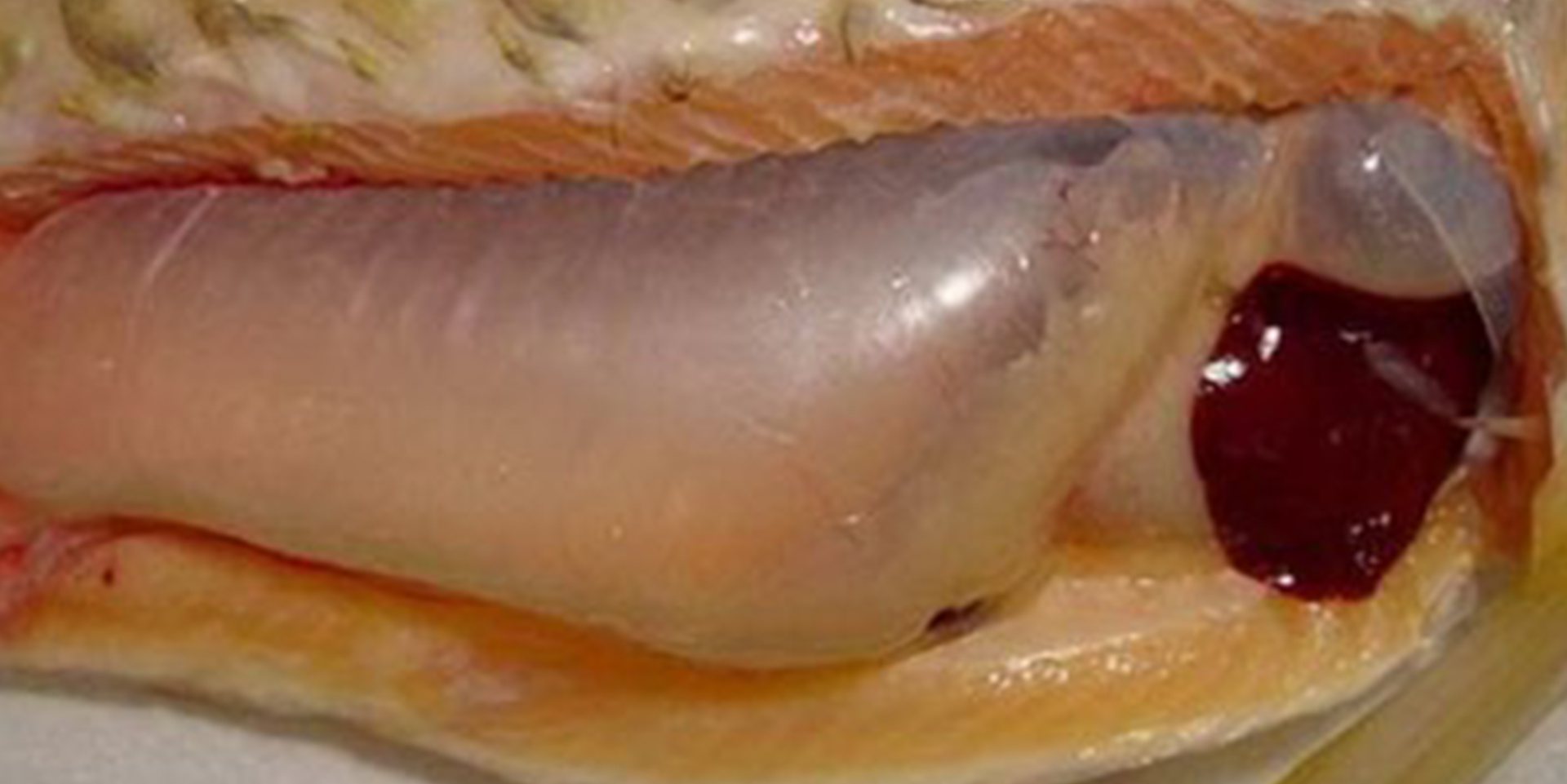
05 Remove the fish maw, and wash under clean water.
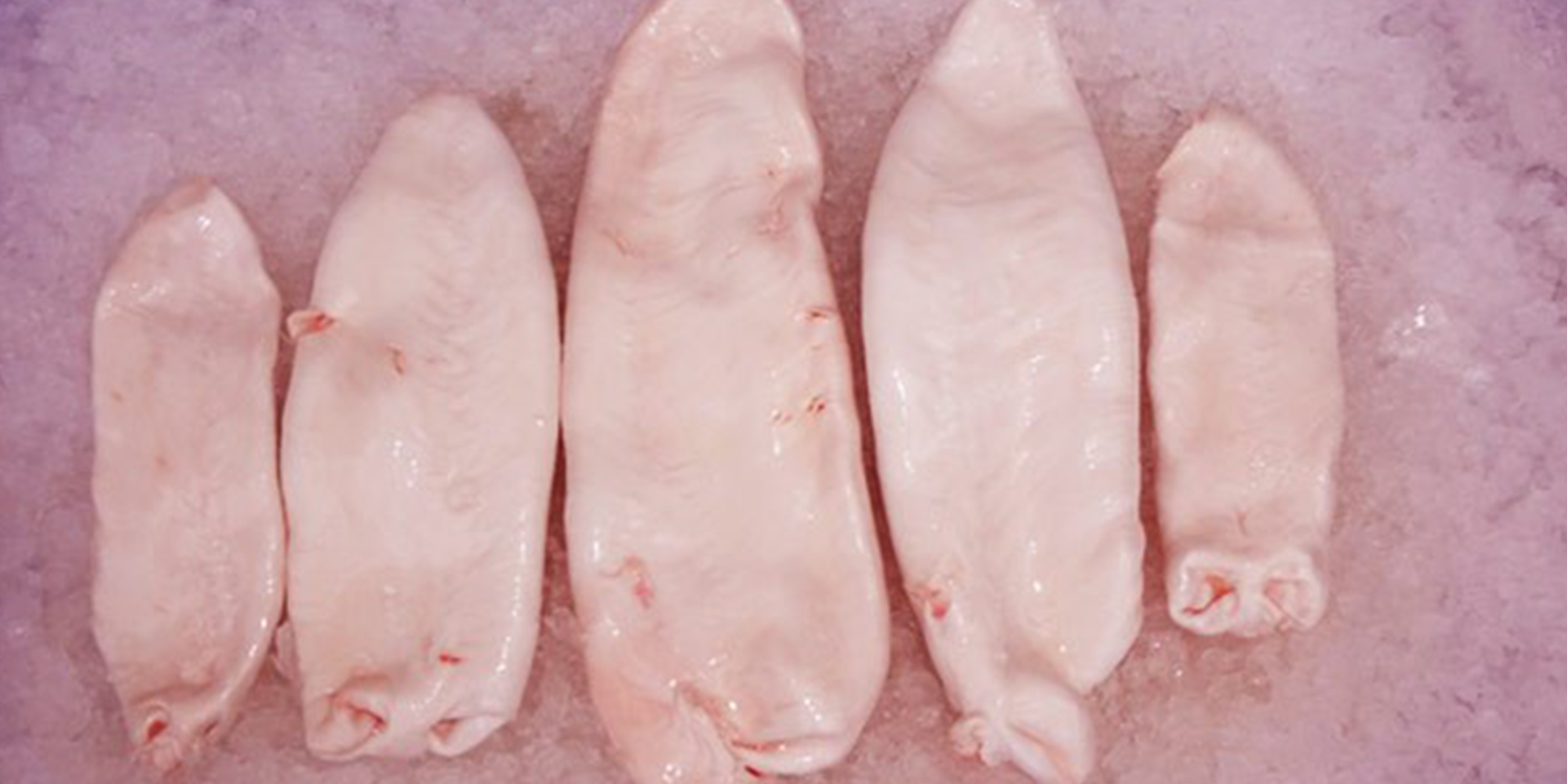
06 After washing, the surface of the fish maw should be scraped to remove the layer of fat attached to it, to prevent it from having a greasy smell after drying.
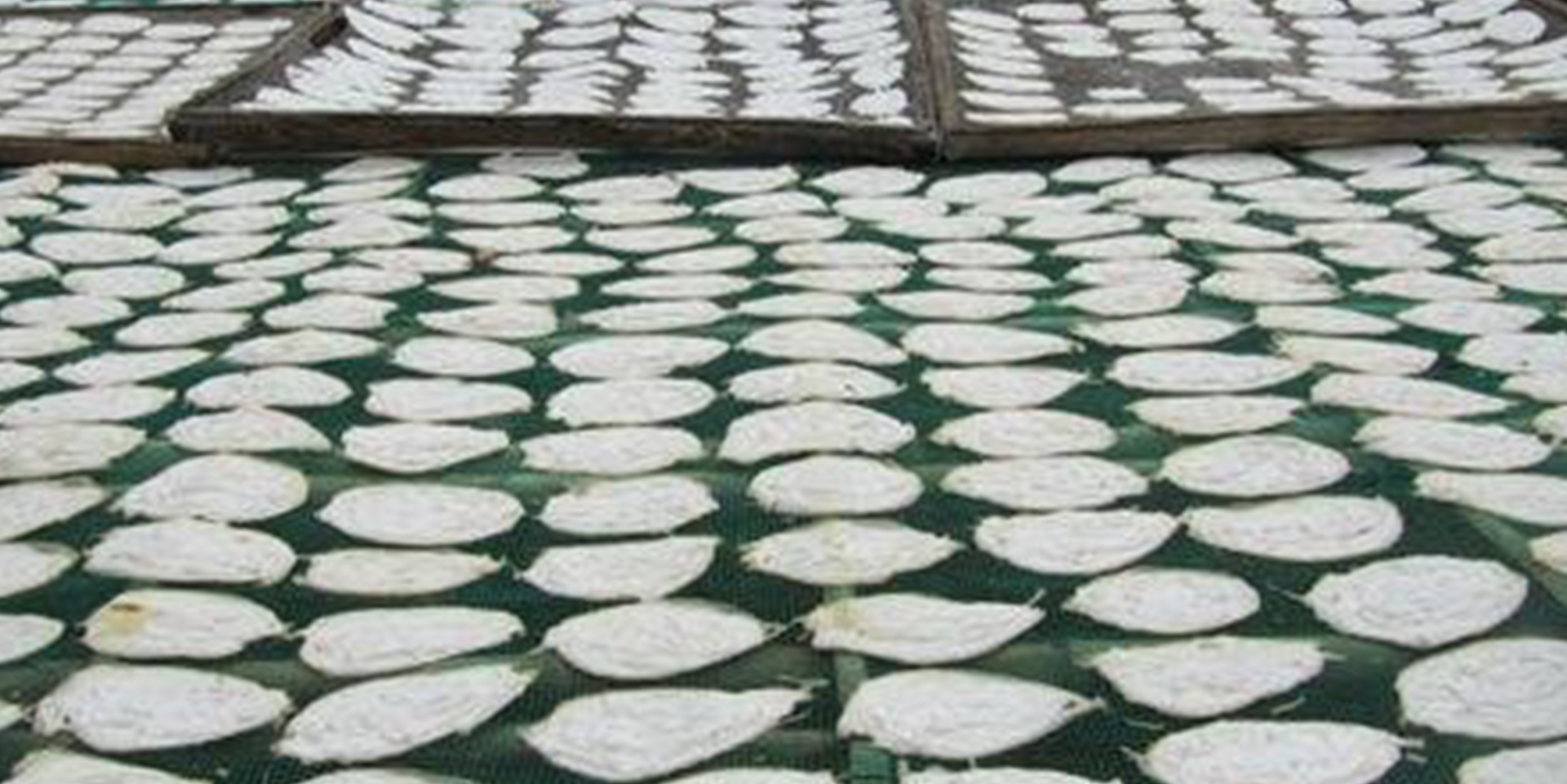

07 The fish maw is sun-dried for several days in a natural environment.
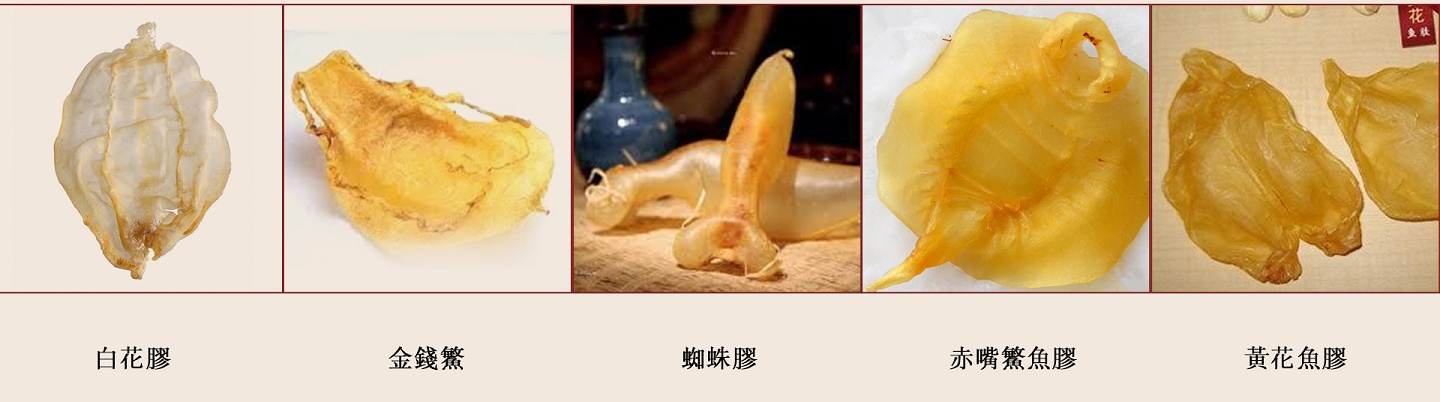

Selection of Fish Maw The selection and pricing of fish maw can vary widely, and the main factors that differentiate them are as follows: fish species, year of production, size and thickness as well as texture.
| SpeciesDifferent fish species have varying body and fiber structures, which result in differences in their fish maw. The fish maw of deep-sea fish species tends to be thicker compared to fish that live in lakes. This is because deep-sea fish have access to a more abundant food source in the ocean compared to fish in lakes. As a result, deep-sea fish maw is generally considered more valuable and has better culinary effects.
|
| Year of ProductionThe gelatin in fish maw gradually settles over time, which is why aged fish maw is commonly referred to as "old fish maw." It has a darker yellow color and is easily digested by the stomach and absorbed by the body, making it more beneficial for health and culinary purposes.
|
| Size
Different sizes of fish maw can also be classified based on the "head count." If the head count is larger, the weight of each individual fish maw will be smaller. The saying “十斤魚一両膠” implies that the weight of fish maw is proportional to the weight of the fish. For example, if the fish maw is a few taels in weight, the fish body itself would weigh several tens of catties (a traditional Chinese unit of weight).
The larger fish species that inhabit deep waters are not easily cultivated, so they tend to have different nutritional characteristics.
|
| Texture
Spider's belly fish maw, eel fish maw, redlip fish maw, and toadfish fish maw are known for their resistance to stewing and become more chewy after stewing. On the other hand, An Nan fish maw and North Sea fish maw become softer after stewing.
|















